Latest Guide to Studying in Japan for Non-Japanese
What are professional schools?
Professional schools are vocational schools which provide students with practical vocational education and advanced technical education. They aim to provide students with the knowledge, technical capabilities, and skills necessary for work and in their actual lives, and to cultivate specialists in a wide range of fields.
Advantages of studying at a Japanese professional school
- You will receive specialized education that is well suited for diverse occupations and which directly helps you find employment.
- You will gain specialized and advanced knowledge and skills that can be used around the world.
- You can gain certifications and go on to find employment in Japan or enter a Japanese university.
Forty-six thousand international students study at professional schools
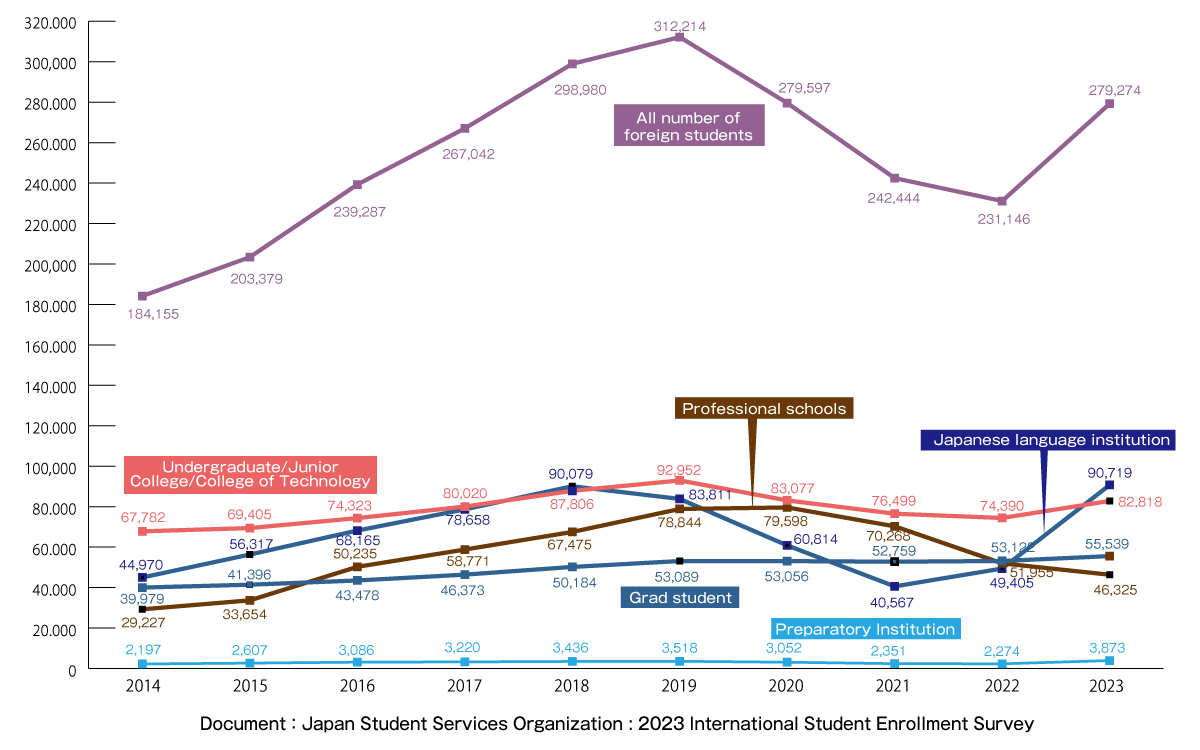
According to a survey by the Japan Student Services Organization (JASSO), around 280,000 international students currently study in Japan, the first time the figure has grown year-on-year since 2019, before the pandemic.
There are 188,000 international students enrolled in professional schools or institutions of higher education such as universities and graduate schools, an increase of 8,000 from the 180,000 international students last year. The number of international students enrolled in professional schools is approximately 46,000, down from 6,000 last year.
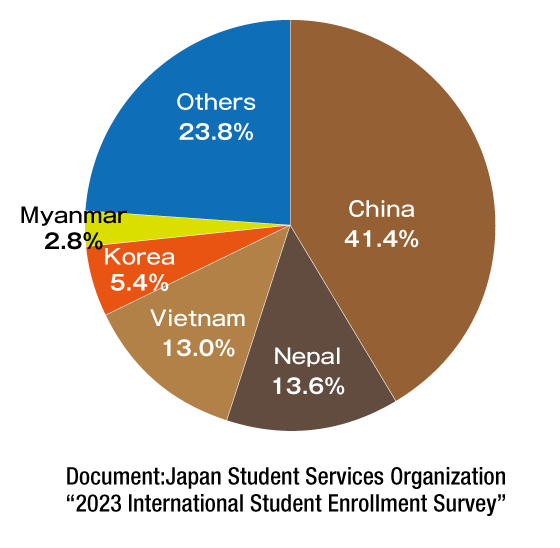
By country/region of origin, 41.4% of the students are from China. This is followed by Nepal at 13.6%, followed by Vietnam, South Korea and Myanmar.
International students wanting to work in Japan are increasing in number
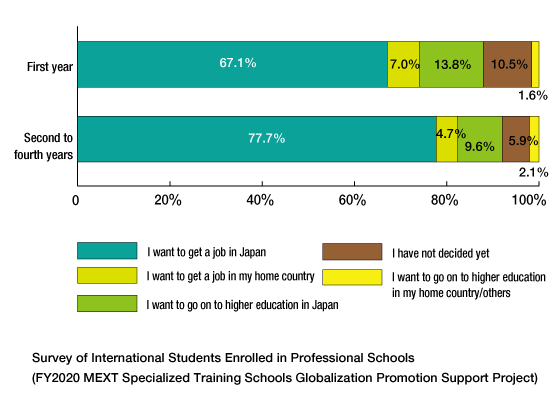
According to the “Survey of International Students Enrolled in Professional Schools" conducted in December 2021 (FY2021 Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology [MEXT] Specialized Training Schools Globalization Promotion Support Project), 70% of the international students who responded said that they want to find a job in Japan.Nearly 80% of the second- to fourth-year students responded that their goal is to find a job in Japan.
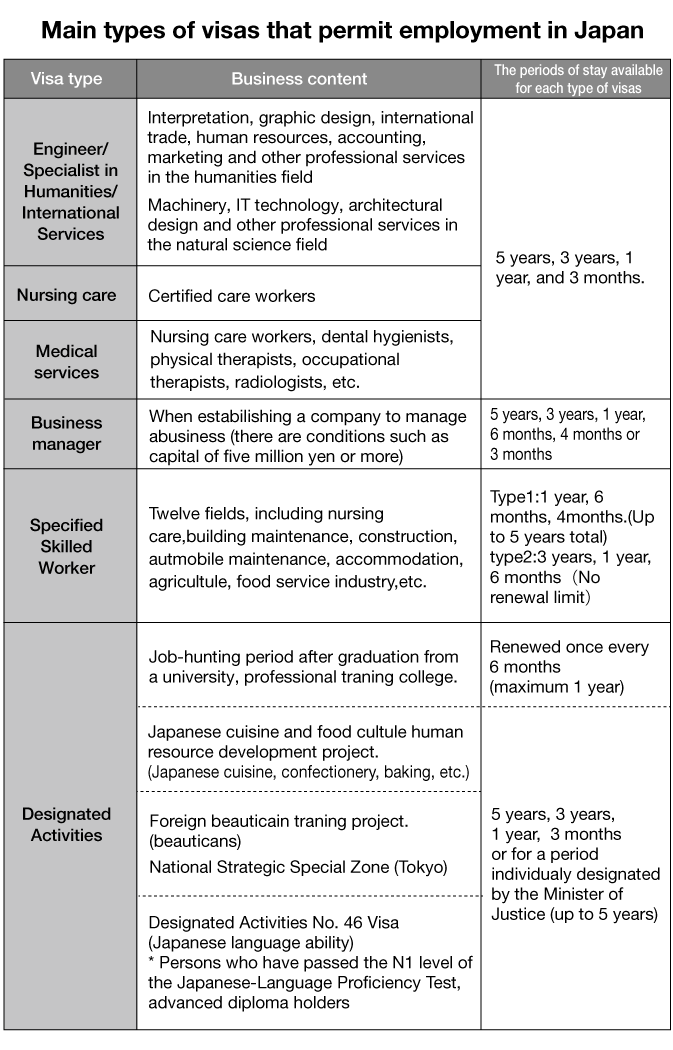
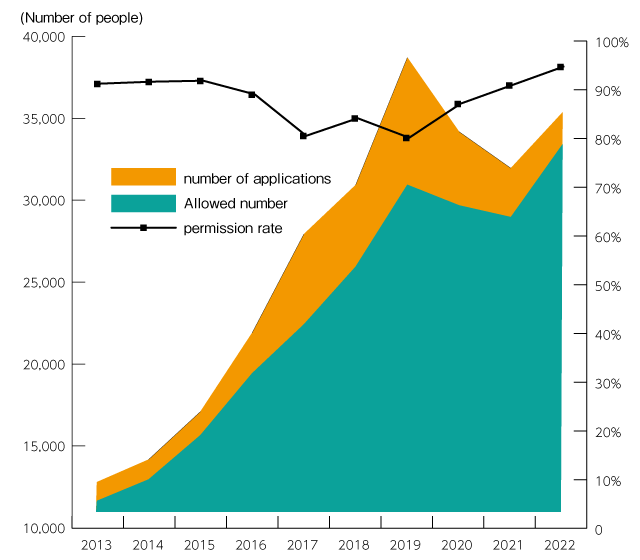
What is the current employment situation for international students who graduated from an educational institute in Japan? International students wanting to work in Japan must change their status of residence from their current student visa. According to “2022 Employment Situation of International Students at Japanese Companies,” a press release from the Immigration Services Agency of Japan (Ministry of Justice), 35,363 international residents with a student visa applied for permission to change their status of residence in 2022 for the purpose of employment at Japanese companies, of which 33,415 were approved. Both figures are up from the previous year.
A breakdown of the number of permits by status of residence shows that 28,853 were for “Engineer/Specialist in humanities/International services,” or 86.3% of the total. Among those, 84.4% were employed in non-manufacturing industries and 15.2% in manufacturing. Their main duties were “translation and interpretation” (16.1%), "information processing and telecommunications” (7.7%), "planning and administration" (7.4%), and “management” (7.0%).
In terms of the final educational background of the international students who changed to work visas, 9,770 (22.9%) were university graduates and 16,191 (48.5%) were specialized training school graduates. Of those employed, 36.5% were employed by companies in Tokyo.
A new status of residence, “Specified skilled worker,” was established in 2019. This visa allows non-Japanese to work in fields they were not previously permitted to enter. However, only fourteen types of industries are permitted when applying for this visa. For more information on this visa, please visit the Immigration Services Agency of Japan websiteor the like.
In the past, there needed to be a strong relationship between an applicant's course of study and the content of the work they would do at their desired place of employment, and applications to change from a student visa to a work visa were sometimes rejected. Under this program, students who graduate from certified professional schools are treated as having graduated from universities, which greatly expands the range of places where they can seek employment.
https://www.mext.go.jp/a_menu/shougai/senshuu/1412546_00015.htm
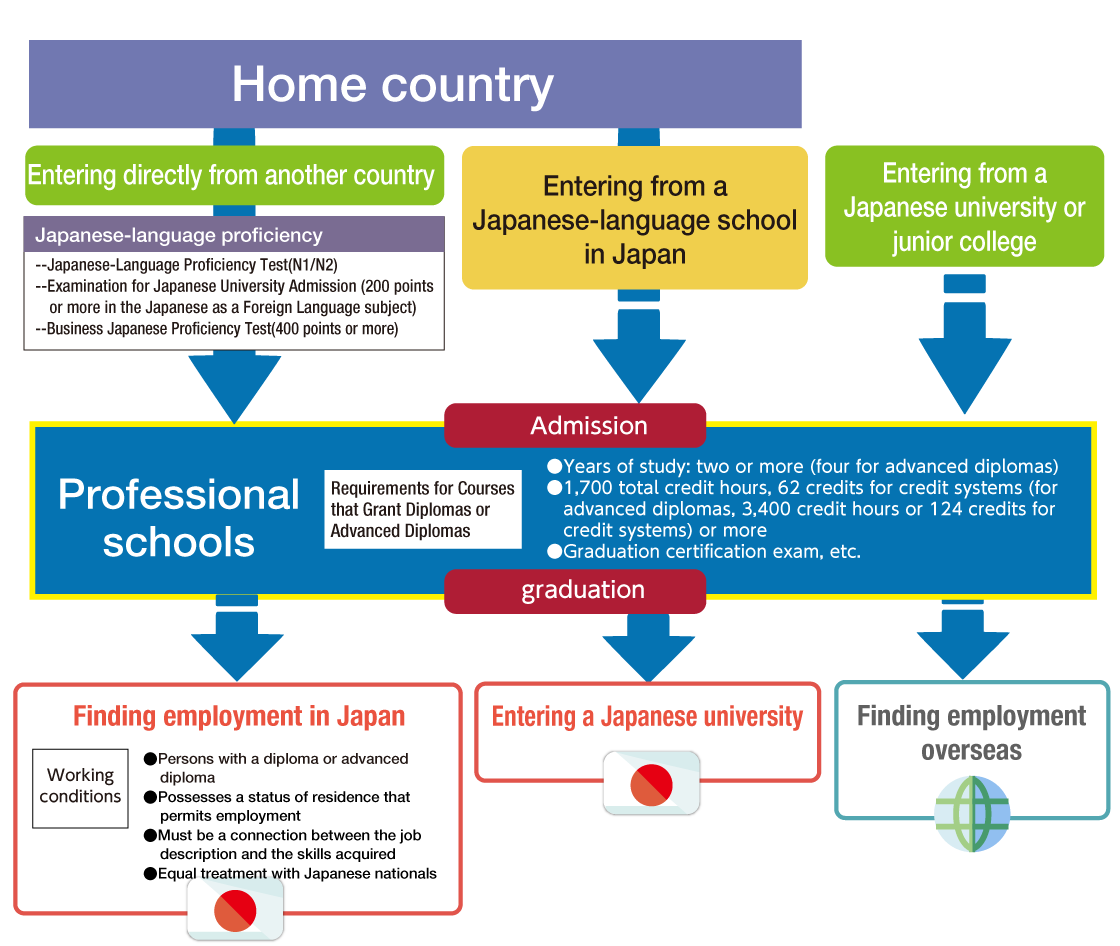
Check points when selecting a professional school
Entering a professional school - Educational and career path after graduating a professional school
Scholarship programs for international students
An honors scholarship of 48,000 yen per month is also available for privately financed students
Scholarships are available from the Japanese government (MEXT) for government-sponsored students and from JASSO for privately financed students. Local governments and private organizations also offer various scholarship programs.
- Payment amount: 117,000 yen per month (FY2022)
- Implementing organization: Government-Sponsored International Student Section, Student and International Student Division, Higher Education Bureau, MEXT
- Tel: 03-5253-4111 (switchboard)
- Implementing organization: http://www.mext.go.jp/
- Payment amount: 48,000 yen per month (FY2021)
- Implementing organization: Honors Scholarship Desk, International Scholarship Division, Student Exchange Department, JASSO
- Tel: 03-5520-6030
- Implementing organization: http://www.jasso.go.jp/
Schools in Tokyo that accept international students
This is a list of schools in the Metropolitan Tokyo Professional Institution Association that accept international students.Click the field you are interested in and a list of schools that accept international students will be displayed with a link to each school’s English or multilingual website.
Engineering/Agriculture
In the engineering field, students study the latest technology and are trained in Japanese monozukuri (craftsmanship). The agricultural field focuses on cultivating biotech professionals.
Relevant courses: Information Systems / Web Design / Video Game Production / Electrical and Electronic Engineering / Mechanical Engineering / Architectural Design / Civil Engineering and Surveying / Automobile Maintenance / Broadcasting Technology / Audio Technology / Optometric Technology / Others Biotechnology
Medicine
Students are trained to work in the medical field as technicians. Since many of these occupations require national certifications, this can lead to lifelong stable employment.Relevant courses: Nursing / Clinical Laboratory / Radiology / Clinical Engineering / Dental Techniques / Dental Hygiene / Physical Therapy / Occupational Therapy / Acupuncture, Moxibustion, Massage, Acupressure / Judo Therapy / Speech Therapy / Vision Training / Others
Hygiene(Nutrition, cooking, confectionery, etc.)
Students are trained to be professionals in the food industry. Many skill training and practical training classes are offered to solidify the students’ foundation and help them find jobs in related industries.
Relevant courses: Nutritionist / Registered Dietitian / Chefs / Culinary Technology and Management / Confectionery Hygienist / Confectionery Technology / Pastry Chef / Japanese Confectionery / Baking Technology / Other
Hygiene(Barber, beauty, etc.)
In addition to training hairdressers and barbers, schools in this field develop personnel who meet the needs of the entire beauty industry, which has been expanding in recent years to include makeup, nail care, esthetics and other services.
Relevant courses: Beauty / Hairdressing / Hair Makeup Artist / Beauty Business / Total Beauty / Esthetics / Makeup / Nail / Bridal
Education and social welfare
These schools train personnel who support the education and welfare fields. Students acquire the specialized knowledge and skills to support these industries, which have a serious shortage of human resources.
Relevant courses: Early Childhood Education / Kindergarten Teacher Training / Childcare / Nursery School Teacher Training / Nursing Welfare / Social Welfare / Child Welfare / Mental Health Welfare
Commercial
Practical education that enables students to become immediate assets in a variety of business fields is offered. There are also diverse curriculums focusing on specific industries.
Relevant courses: Accountant / Certified Public Tax Accountant / Bookkeeping / Management and Business / Medical Administration / Pharmaceutical Administration / Trading Business / Hotel / Tourism Business / Flight Attendant / Railway & Transportation / Bridal / Other
Apparel and household management
Many courses cover the wide range of occupations related to the fashion industry. Students acquire solid skills and an independent sense of design.
Relevant courses: Fashion Design / Fashion Business / Apparel / Fashion Technical / Pattern Maker / Stylist / Kimono
Culture and liberal arts
This field includes a wide variety of specialties such as graphic design, fine arts, animation and other arts, languages, sports, and animal- and law-related occupations.
Relevant courses: Language / Graphic Design / Product Design / Photography / Painting / Manga / Broadcasting / Cinema / Sound / Lighting / Dance / Theater / Voice Acting / Sports / Civil service / Other
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT STUDYING IN JAPAN
This pamphlet was created by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government for those who want to study abroad at a Japanese school.
CONTENTS
Ⅰ.How should I prepare for studying in Japan?
- How does the Japanese education system work?
- How many international students from abroad are currently studying in Japan?
- What are the requirements for studying in Japan?
- How much money will I need for my school expenses?
- What is the status of residence? What kind of status of residence do I need to study in Japan?
Ⅱ.At what school should I study?
- What is a Japanese language Institute?
- What are the requirements for entering graduate school?
- What are the requirements for entering university?
- What are the requirements for entering junior college?
- What are the requirements for entering college of technology?
- What are the requirements for entering specialized training college,postsecondary courses (professional training college)?
- Are there any scholarship programs available for international students?
- Can I find a job in Japan?
Ⅲ.Will I be alright while living in Japan?
- What exactly is a “residence card”?
- What is the cost of living in Japan?
- Can international students work part-time?
- What procedures do I need to follow to be able to use the electricity, gas,tap water and telephone services?
- When and how do I put my garbage out? (Garbage and recycling)
- What do I need to do in emergencies?
- Do I need to enroll in Health Insurance and Pension plan?
- What is an “Individual Number”?
- What kind of procedures do I need to follow while studying in Japan?
- What are the things that international students need to be careful about?